2016 Java Chapter 10 (Week 10)
From: 2016-09-01 00:00:00
To: 2016-12-07 00:00:00
Now: 2024-11-21 21:52:26
Status: Public
E - 기하: Triangle2D 클래스
Time Limit: 1s
Memory Limit: 128MB
Snippet Judge Submissions: 1465 Solved: 344
- Description
다음 내용을 포함하는 Triangle2D 클래스를 만들어보자.
- MyPoint형의 세 점 p1, p2, p3필드를 설정하고 반환하는 메소드를 가진다. MyPoint 타입은 Programming Exercise 10.4에 정의되어있습니다.
- 세 점의 좌표를 각각 (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 5)로 가지는 default 삼각형을 만드는 무(無)인자(no-arg) 생성자를 가진다.
- 특정한 좌표를 가지는, 삼각형을 만드는 생성자를 가진다.
- 삼각형의 넓이를 반환하는 getArea() 메소드를 가진다.
- 삼각형의 둘레를 반환하는 getPerimeter() 메소드를 가진다.
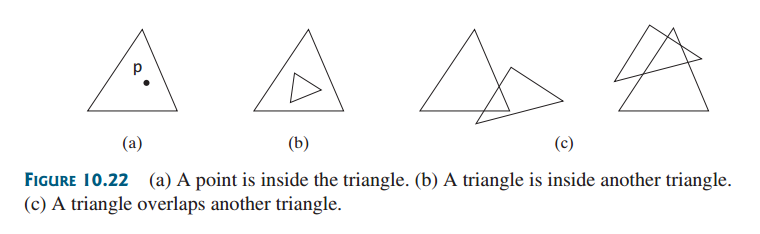
- 특정한 점 p가 이 삼각형 안에 있으면 true를 반환하는 contains(MyPoint p) 메소드를 가진다. (Figure 10.22a)
- 특정한 삼각형이 이 삼각형 안에 있으면 true를 반환하는 contains(Triangle2D t) 메소드를 가진다. (Figure 10.22b)
- 특정한 삼각형이 이 삼각형과 겹치면 true를 반환하는 overlaps(Triangle2D t) 메소드를 가진다. (Figure 10.22c)
- Three points named p1, p2, and p3 of the type MyPoint with getter and setter methods. MyPoint is defined in Programming Exercise 10.4.
- A no-arg constructor that creates a default triangle with the points (0, 0), (1, 1), and (2, 5).
- A constructor that creates a triangle with the specified points.
- A method getArea() that returns the area of the triangle.
- A method getPerimeter() that returns the perimeter of the triangle.
- A method contains(MyPoint p) that returns true if the specified point p is inside this triangle (see Figure 10.22a).
- A method contains(Triangle2D t) that returns true if the specified triangle is inside this triangle (see Figure 10.22b).
- A method overlaps(Triangle2D t) that returns true if the specified triangle overlaps with this triangle (see Figure 10.22c).
여러분이 작성한 코드는 아래 샘플코드의 YOUR_CODE 부분에 들어가 컴파일 됩니다.
- Input
* Line 1 : 테스트케이스 T (1~1,000)
* Line 2 ~ T+1 : x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4 x5 y5 x6 y6 x7 y7 (공백으로 구분된 14개의 실수)
- 실수의 범위는 -100 ~ 100
- x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3는 삼각형 r1의 정점
- x4 y4 x5 y5 x6 y6는 삼각형 r2의 정점
- x7 y7는 정점 p
- r1과 r2는 항상 삼각형
- Output
* Line 1 ~ 4T : 각 테스트 케이스마다 샘플 출력과 같이 4줄씩 출력
- Line 3 : r1이 p를 포함하면 true 아니라면 false
- Line 4 : r1이 r2를 포함하면 contain, r1와 r2가 겹치면 overlaps, 만나지 않는다면 no overlap을 출력
- Sample Code
-
import javafx.geometry.*; import java.awt.geom.Line2D; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int T = sc.nextInt(); for (int t = 0; t < T; t++) { double x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, x5, y5, x6, y6, x7, y7; x1 = sc.nextDouble(); y1 = sc.nextDouble(); x2 = sc.nextDouble(); y2 = sc.nextDouble(); x3 = sc.nextDouble(); y3 = sc.nextDouble(); x4 = sc.nextDouble(); y4 = sc.nextDouble(); x5 = sc.nextDouble(); y5 = sc.nextDouble(); x6 = sc.nextDouble(); y6 = sc.nextDouble(); x7 = sc.nextDouble(); y7 = sc.nextDouble(); Triangle2D r1 = new Triangle2D(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3); Triangle2D r2 = new Triangle2D(x4, y4, x5, y5, x6, y6); System.out.printf("Area is %.1f\n", r1.getArea()); System.out.printf("Perimeter is %.1f\n", r1.getPerimeter()); System.out.println(r1.contains(x7, y7)); if (r1.contains(r2)) { System.out.println("contain"); } else if (r1.overlaps(r2)) { System.out.println("overlaps"); } else { System.out.println("no overlap"); } } } } YOUR_CODE - Sample Input
-
3 -2 0 0 2 2 0 -1 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 -1 0 0 1 1 0 -2 0 0 2 2 0 2 0 -2 0 0 2 2 0 -1 -1 0 -2 1 -1 -1 1
- Sample Output
-
Area is 4.0 Perimeter is 9.7 true contain Area is 1.0 Perimeter is 4.8 false overlaps Area is 4.0 Perimeter is 9.7 true no overlap
- Source
JAVA2015 PE10.12